Shingles Disease: How This Deadly Viral Infection is Related to Chickenpox? Know Symptoms, Treatments, and more
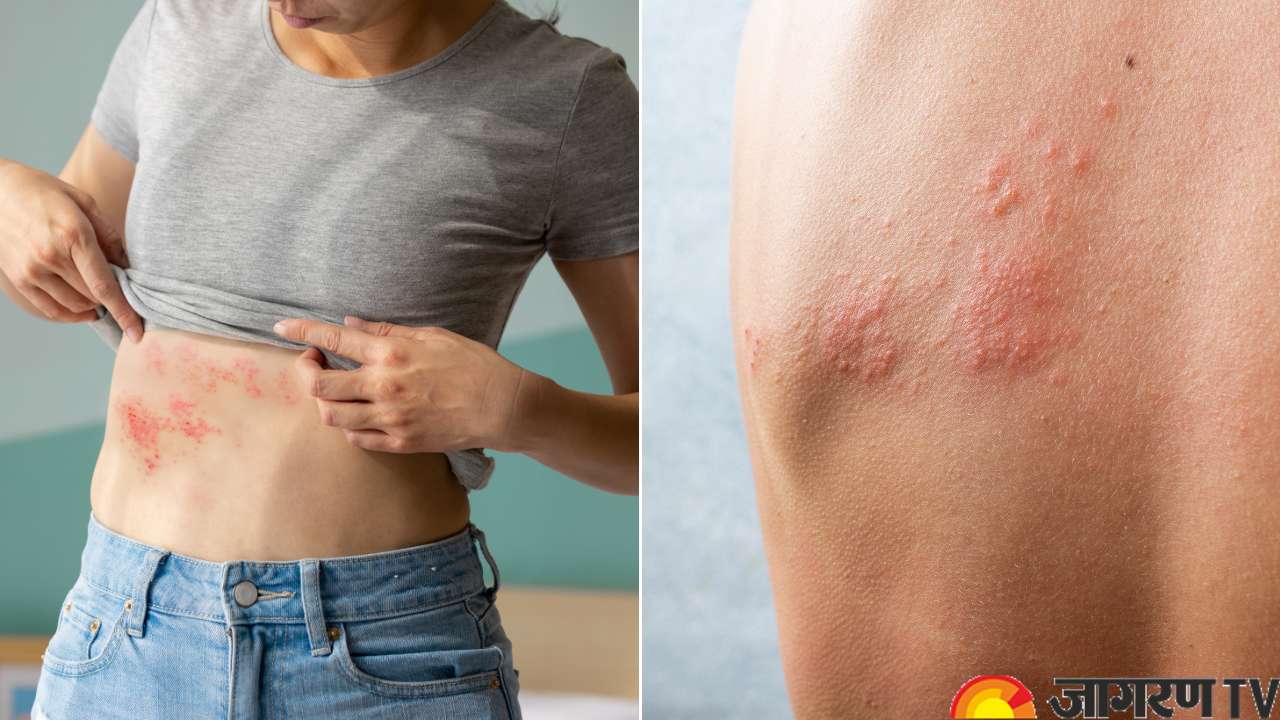

Herpes Zoster Disease: Shingles, commonly known as herpes zoster, is a painful viral infection that can affect anybody who has previously suffered from chickenpox. Shingles is a virus infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus, which is also responsible for chickenpox. The virus can remain inactive in nerve tissues for years after a person recovers from chickenpox. Later, it can reactivate and develop shingles, which is characterised by a painful rash and other symptoms.
Symptoms of Shingles
The most common symptom of the shingles disease is a painful rash. The rash often develops on one side of the body or on the face and follows a nerve route. The rash may begin as tiny red acne-like spots that grow into blisters filled with fluid. Some of the symptoms of Shingles include:
-
Burning, tingling, or itching in a specific part of the body
-
Sensitivity to touch or temperature changes
-
A red rash that begins as a single stripe or band on one side of the body and develops into fluid-filled blisters that ultimately crust over
-
Flu-like symptoms such as fever, headache, drowsiness, nausea, and generalised achiness
-
Sharp and stabbing pain along the damaged nerve
-
Postherpetic neuralgia (chronic nerve pain) can occur after the rash has healed.
Age Group at Risk
Shingles can happen to anybody at any age but it is more frequent in older people, especially those aged above 50. People may have weakened immune systems as they age, increasing their vulnerability to shingles. Additionally, people whose immune systems have been affected by illnesses or medications are also at a higher risk.
Shingles Treatment
Despite shingles is often a self-limiting condition, it can also result in postherpetic neuralgia, a severe and protracted nerve pain in the afflicted area, as well as bacterial skin infections. Early diagnosis, treatment, and vaccination can reduce the severity of the illness and its duration, as well as the likelihood of complications.
Antiviral Medications
Acyclovir, valacyclovir, or famciclovir are antiviral medications that can help to lessen the duration and intensity of the rash as well as the discomfort.
Pain Medications
To address the discomfort caused by shingles, over-the-counter or prescription pain medicines may be prescribed.
Topical Creams
Calamine lotion or numbing lotions can alleviate itching and pain.
Postherpetic Neuralgia Treatment
Treatments like medication, nerve blocks, or physical therapy could be required if postherpetic neuralgia develops.
Shingles Vaccine
Vaccination is among the best methods for preventing shingles. Even if a person has had shingles before or has had the earlier Zostavax shingles vaccination, people above 50 are advised to get the shingles vaccine, known as Shingrix. Shingrix is a two-dose vaccination that is given over the course of many months and provides more effective protection against shingles and associated side effects.
Related videos
-
Sustainable Fashion Tips: 5 Ways To Style Better Through An Eco-Conscious Route ...
-
World Wind Day 2025: Role of Wind Energy in Sustainable Development, Know its Positive Impact ...
-
Father's Day 2025 : फादर्स डे को अपने पिता के लिए यादगार, ऐसे ...
-
Summer Care Tips: Benefits of Gond Katira in Keeping Your Body Hydrated and Cool in ...