What is Hepatitis: Common Types of Hepatitis, Their Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and More
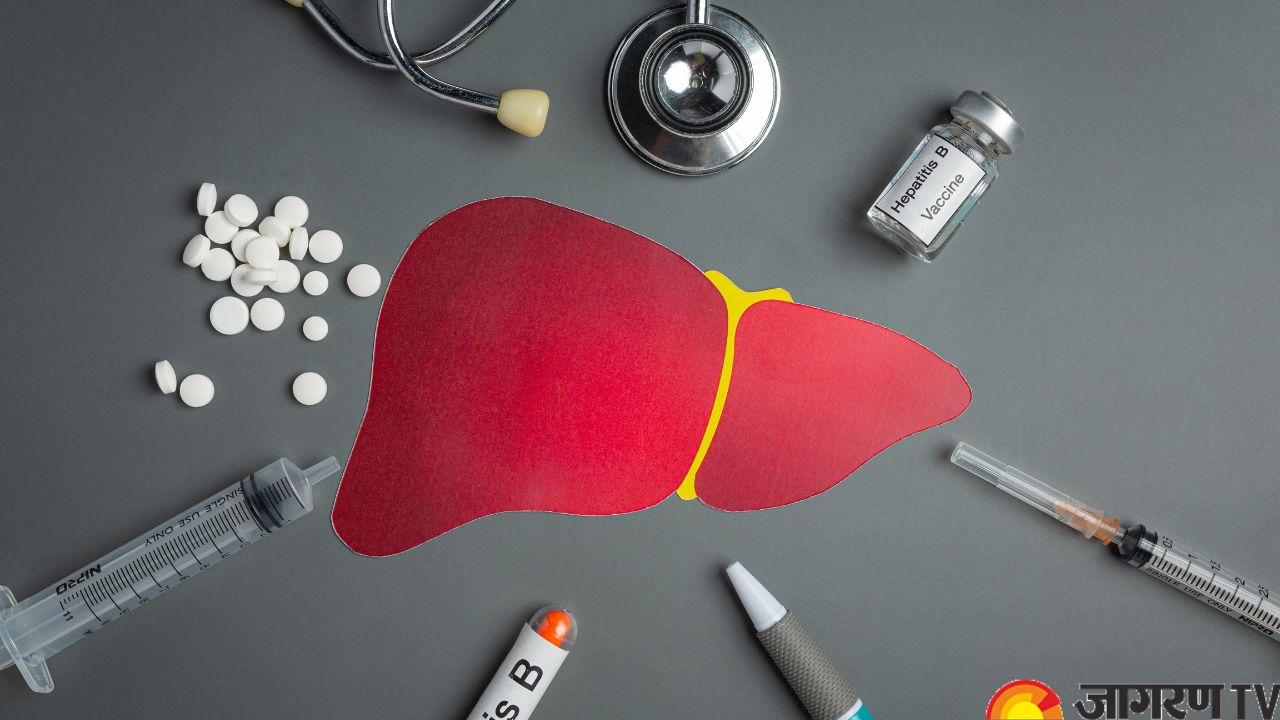
Hepatitis Types: Hepatitis is a viral infection that affects millions around the world. It refers to liver inflammation, which is most commonly caused by viral infections. It can also be caused by exposure to toxic substances, autoimmune diseases, or alcohol abuse. The liver is a vital organ that filters toxins, produces bile, and stores nutrients. Hepatitis compromises the liver’s ability to function by causing inflammation, leading to serious health consequences. While common types of Hepatitis are A, B, and C, there are 5 main types of Hepatitis.
Let us delve deeper into the types of Hepatitis, their causes, symptoms, and more.
Types of Hepatitis
Viral hepatitis comes in five primary forms: A, B, C, D, and E. Each variety has a unique mode of transmission, set of symptoms, and effect on health, and is caused by a different virus.
Hepatitis A (HAV)
Hepatitis A is caused by the hepatitis A virus, which is primarily transmitted through the consumption of contaminated food and water or close contact with an infected individual. Common symptoms that appear 2 to 6 weeks after exposure include fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dark urine, joint pain, and jaundice. HAV can be avoided by vaccinating, practicing good hygiene, and providing access to clean water.
Hepatitis B (HBV)
Hepatitis B is caused by the hepatitis B virus, which spreads through contact with infectious body fluids such as blood, sperm, and vaginal secretions. Unprotected sex, needle sharing, and passing from mother to baby during childbirth are all common routes of transmission. Symptoms can include fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dark urine, joint pain, and jaundice. Chronic HBV can cause severe liver damage, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. Hepatitis B can be avoided by getting vaccinated, practicing safe sex, not sharing needles, and ensuring safe blood transfusions.
Hepatitis C (HCV)
Hepatitis C is caused by the hepatitis C virus, which is primarily transmitted through contact with infected blood. This can happen by sharing needles, unsterile medical equipment, or, less commonly, sexual contact or from mother to baby during childbirth. Many HCV patients are asymptomatic or have mild symptoms, but chronic infection can result in liver damage, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. Symptoms may include fatigue, fever, nausea, loss of appetite, abdominal pain, dark urine, and jaundice. Although there is no vaccine for HCV, preventive measures include not sharing needles, following safe medical practices, and screening blood products.
Hepatitis D (HDV)
Hepatitis D is caused by the hepatitis D virus, which only infects people who are already infected with HBV, as HDV requires HBV to replicate. HDV symptoms are similar to HBV but more severe. Symptoms may include fever, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dark urine, joint pain, and jaundice. Vaccination, avoiding contact with infected blood, and following safe medical practices can all help prevent HBV.
Hepatitis E (HEV)
Hepatitis E is caused by the hepatitis E virus, which is primarily transmitted through the consumption of contaminated water or raw meat. The symptoms are similar to HAV, such as fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dark urine, joint pain, and jaundice. HEV is typically acute and self-limiting but can be severe in pregnant women. Preventive measures include providing access to clean water, maintaining proper sanitation, and eating properly cooked meat.
Related videos
-
Liver Care: All You Need to Know About Your Liver, Functions, Common Liver Problems, and ...
-
World Hepatitis Day 2024: How Hepatitis Spreads? Know Causes, Symptoms, Types, and More ...
-
World Liver Day 2023: Do you have a Fatty Liver? Know the signs of Fatty ...
-
World Hepatitis Day 2022: Date, Significance and Theme of this year ...